Thermal Energy Storage Market Growth: Driving the Future of Renewable Integration
Thermal Energy Storage Market: Growth Dynamics, Key Trends & Future Outlook
Market Estimation & Definition
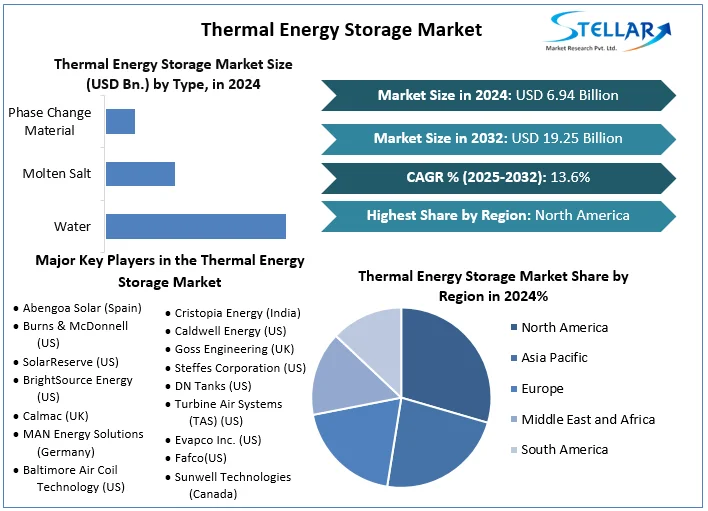
The Thermal Energy Storage (TES) market refers to technologies that store thermal energy — either heat or cold — for later use in power generation, industrial processes, building heating/cooling, and renewable energy integration. TES systems enable energy captured during low‑demand or peak generation periods to be deployed when needed, improving efficiency, flexibility, and grid reliability. These systems use mediums such as water, molten salt, and phase change materials to store energy through sensible heat, latent heat, or thermochemical processes.
In 2024, the global thermal energy storage market was valued at approximately USD 6.94 billion. It is projected to grow to around USD 19.25 billion by 2032, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 13.6 % through 2032, driven by increasing renewable energy penetration and rising demand for grid‑scale storage solutions.
Purchase This Research Report at up to 30% Off @ https://www.stellarmr.com/report/req_sample/Thermal-Energy-Storage-Market/356
Market Growth Drivers & Opportunity
A key growth driver for the TES market is the integration with renewable energy sources, especially solar thermal and concentrated solar power (CSP). Because solar generation is intermittent, storing excess heat for use during non‑sunlight hours enhances energy reliability and enables continuous power generation from renewable energy. TES systems are essential in CSP plants to prolong generation beyond daylight hours.
Decarbonization and energy transition goals globally are pushing utilities, governments, and industries to adopt storage solutions that reduce dependence on fossil fuels and balance supply‑demand variability in grids with high shares of wind and solar. TES helps to lower carbon emissions by shifting energy supply from peak fossil fuel generation to stored renewable heat or cold.
Opportunities also arise from the growing district heating and cooling applications, where thermal storage decouples generation from demand, enabling seasonal and peak load management to reduce overall energy consumption in buildings and industry.
What Lies Ahead: Emerging Trends Shaping the Future
Several trends are poised to shape TES market growth in the coming years:
• Advancement in materials and technology — Thermochemical storage and enhanced phase change materials (PCMs) are gaining interest for their high energy density and long‑term stability, offering efficiency improvements over traditional methods.
• Grid‑scale integration with renewables — As energy systems expand solar and wind capacity, TES solutions will be increasingly deployed alongside digital grid platforms and smart energy management systems to balance intermittent outputs.
• Cold storage and HVAC innovation — Ice and chilled water storage systems are being adopted for sustainable cooling solutions in large buildings and data centers, which helps flatten peak electricity demand and improve efficiency.
• Policy and incentive support — Government incentives and regulatory frameworks aimed at decarbonization and energy efficiency are expected to accelerate TES adoption in utility and industrial applications.
Purchase This Research Report at up to 30% Off @ https://www.stellarmr.com/report/req_sample/Thermal-Energy-Storage-Market/356
Segmentation Analysis from the URL
According to the industry report, the thermal energy storage market is segmented across type, technology, application, and end‑user.
By Type:
• Water — Common in sensible heat storage due to low cost and simplicity.
• Molten Salt — Widely used in CSP and high‑temperature industrial applications.
• Phase Change Material — Stores and releases energy at specific phase transition temperatures to enhance efficiency.
By Technology:
• Sensible Heat Storage — Dominates due to maturity and cost‑effectiveness for large thermal loads.
• Latent Heat Storage — Efficient for moderate temperature applications.
• Thermochemical Storage — Emerging for high‑density, long‑duration storage.
About us
Phase 3,Navale IT Zone, S.No. 51/2A/2,
Office No. 202, 2nd floor,
Near, Navale Brg,Narhe,
Pune, Maharashtra 411041
sales@stellarmr.com
Thermal Energy Storage Market: Growth Dynamics, Key Trends & Future Outlook
Market Estimation & Definition
The Thermal Energy Storage (TES) market refers to technologies that store thermal energy — either heat or cold — for later use in power generation, industrial processes, building heating/cooling, and renewable energy integration. TES systems enable energy captured during low‑demand or peak generation periods to be deployed when needed, improving efficiency, flexibility, and grid reliability. These systems use mediums such as water, molten salt, and phase change materials to store energy through sensible heat, latent heat, or thermochemical processes.
In 2024, the global thermal energy storage market was valued at approximately USD 6.94 billion. It is projected to grow to around USD 19.25 billion by 2032, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 13.6 % through 2032, driven by increasing renewable energy penetration and rising demand for grid‑scale storage solutions.
Purchase This Research Report at up to 30% Off @ https://www.stellarmr.com/report/req_sample/Thermal-Energy-Storage-Market/356
Market Growth Drivers & Opportunity
A key growth driver for the TES market is the integration with renewable energy sources, especially solar thermal and concentrated solar power (CSP). Because solar generation is intermittent, storing excess heat for use during non‑sunlight hours enhances energy reliability and enables continuous power generation from renewable energy. TES systems are essential in CSP plants to prolong generation beyond daylight hours.
Decarbonization and energy transition goals globally are pushing utilities, governments, and industries to adopt storage solutions that reduce dependence on fossil fuels and balance supply‑demand variability in grids with high shares of wind and solar. TES helps to lower carbon emissions by shifting energy supply from peak fossil fuel generation to stored renewable heat or cold.
Opportunities also arise from the growing district heating and cooling applications, where thermal storage decouples generation from demand, enabling seasonal and peak load management to reduce overall energy consumption in buildings and industry.
What Lies Ahead: Emerging Trends Shaping the Future
Several trends are poised to shape TES market growth in the coming years:
• Advancement in materials and technology — Thermochemical storage and enhanced phase change materials (PCMs) are gaining interest for their high energy density and long‑term stability, offering efficiency improvements over traditional methods.
• Grid‑scale integration with renewables — As energy systems expand solar and wind capacity, TES solutions will be increasingly deployed alongside digital grid platforms and smart energy management systems to balance intermittent outputs.
• Cold storage and HVAC innovation — Ice and chilled water storage systems are being adopted for sustainable cooling solutions in large buildings and data centers, which helps flatten peak electricity demand and improve efficiency.
• Policy and incentive support — Government incentives and regulatory frameworks aimed at decarbonization and energy efficiency are expected to accelerate TES adoption in utility and industrial applications.
Purchase This Research Report at up to 30% Off @ https://www.stellarmr.com/report/req_sample/Thermal-Energy-Storage-Market/356
Segmentation Analysis from the URL
According to the industry report, the thermal energy storage market is segmented across type, technology, application, and end‑user.
By Type:
• Water — Common in sensible heat storage due to low cost and simplicity.
• Molten Salt — Widely used in CSP and high‑temperature industrial applications.
• Phase Change Material — Stores and releases energy at specific phase transition temperatures to enhance efficiency.
By Technology:
• Sensible Heat Storage — Dominates due to maturity and cost‑effectiveness for large thermal loads.
• Latent Heat Storage — Efficient for moderate temperature applications.
• Thermochemical Storage — Emerging for high‑density, long‑duration storage.
About us
Phase 3,Navale IT Zone, S.No. 51/2A/2,
Office No. 202, 2nd floor,
Near, Navale Brg,Narhe,
Pune, Maharashtra 411041
sales@stellarmr.com
Thermal Energy Storage Market Growth: Driving the Future of Renewable Integration
Thermal Energy Storage Market: Growth Dynamics, Key Trends & Future Outlook
Market Estimation & Definition
The Thermal Energy Storage (TES) market refers to technologies that store thermal energy — either heat or cold — for later use in power generation, industrial processes, building heating/cooling, and renewable energy integration. TES systems enable energy captured during low‑demand or peak generation periods to be deployed when needed, improving efficiency, flexibility, and grid reliability. These systems use mediums such as water, molten salt, and phase change materials to store energy through sensible heat, latent heat, or thermochemical processes.
In 2024, the global thermal energy storage market was valued at approximately USD 6.94 billion. It is projected to grow to around USD 19.25 billion by 2032, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 13.6 % through 2032, driven by increasing renewable energy penetration and rising demand for grid‑scale storage solutions.
Purchase This Research Report at up to 30% Off @ https://www.stellarmr.com/report/req_sample/Thermal-Energy-Storage-Market/356
Market Growth Drivers & Opportunity
A key growth driver for the TES market is the integration with renewable energy sources, especially solar thermal and concentrated solar power (CSP). Because solar generation is intermittent, storing excess heat for use during non‑sunlight hours enhances energy reliability and enables continuous power generation from renewable energy. TES systems are essential in CSP plants to prolong generation beyond daylight hours.
Decarbonization and energy transition goals globally are pushing utilities, governments, and industries to adopt storage solutions that reduce dependence on fossil fuels and balance supply‑demand variability in grids with high shares of wind and solar. TES helps to lower carbon emissions by shifting energy supply from peak fossil fuel generation to stored renewable heat or cold.
Opportunities also arise from the growing district heating and cooling applications, where thermal storage decouples generation from demand, enabling seasonal and peak load management to reduce overall energy consumption in buildings and industry.
What Lies Ahead: Emerging Trends Shaping the Future
Several trends are poised to shape TES market growth in the coming years:
• Advancement in materials and technology — Thermochemical storage and enhanced phase change materials (PCMs) are gaining interest for their high energy density and long‑term stability, offering efficiency improvements over traditional methods.
• Grid‑scale integration with renewables — As energy systems expand solar and wind capacity, TES solutions will be increasingly deployed alongside digital grid platforms and smart energy management systems to balance intermittent outputs.
• Cold storage and HVAC innovation — Ice and chilled water storage systems are being adopted for sustainable cooling solutions in large buildings and data centers, which helps flatten peak electricity demand and improve efficiency.
• Policy and incentive support — Government incentives and regulatory frameworks aimed at decarbonization and energy efficiency are expected to accelerate TES adoption in utility and industrial applications.
Purchase This Research Report at up to 30% Off @ https://www.stellarmr.com/report/req_sample/Thermal-Energy-Storage-Market/356
Segmentation Analysis from the URL
According to the industry report, the thermal energy storage market is segmented across type, technology, application, and end‑user.
By Type:
• Water — Common in sensible heat storage due to low cost and simplicity.
• Molten Salt — Widely used in CSP and high‑temperature industrial applications.
• Phase Change Material — Stores and releases energy at specific phase transition temperatures to enhance efficiency.
By Technology:
• Sensible Heat Storage — Dominates due to maturity and cost‑effectiveness for large thermal loads.
• Latent Heat Storage — Efficient for moderate temperature applications.
• Thermochemical Storage — Emerging for high‑density, long‑duration storage.
About us
Phase 3,Navale IT Zone, S.No. 51/2A/2,
Office No. 202, 2nd floor,
Near, Navale Brg,Narhe,
Pune, Maharashtra 411041
sales@stellarmr.com
0 Commenti
0 condivisioni
184 Views
0 Anteprima